Sensor Network Configuration
All devices in your D4 RTLS are connected by means of network cables and require a network connection to exchange data. They must also be able to connect to a Location Platform server in order to obtain configuration information for booting.
By default, each device receives its IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway from a DHCP server. (If you do not have a DHCP server, see Setting Up DHCP Servers for further information and an example configuration.)
Alternatively, you can configure a device to connect to the Location Platform server by assigning:
-
A static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
-
A DNS configuration, which can contain up to four DNS server IP addresses and up to four suffixes to use.
- A particular search order, which contains a sequence of different methods, such as a simple domain name, fully qualified domain name, IP address, or broadcast, which the device can use to contact the Location Platform server.
From DIMENSION4 3.7 SP1 onwards, sensors will boot reliably on networks where the Ethernet switches are configured with Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and 802.1x / MAB. For information on how the sensor boot process relates to 802.1x / MAB and STP and how to configure recommended timeouts to support sensors using DHCP on a typical switch see
Creating a Search Order
The search methods that you can use are listed in the following table.
| Search Method | Device connects to the network by... |
|---|---|
| Simple domain name | Using a domain name that resolves to an IP address known to the DNS server. |
| Fully-qualified domain name | Using a domain name that specifies its exact location in the tree hierarchy of the Domain Name System (DNS). |
| IP Address | Using the IP address of the Location Platform server. |
| Broadcast | Searching for any available Location Platform server on the same sub network. |
To set up a search order:
-
On the Sensor network configuration tab, add a new search order, ensuring that you provide a unique name for the search order.
-
Add the required search methods in the order that they should be used.
-
Review the details that you have typed.
It is not possible to modify a search order after you save it. To modify an existing search order, you must delete it and then create a new search order with the required settings.
-
Save the search order. The new search order appears on the list of Search Orders. You can add the search order to the required devices.
Creating a DNS Configuration
To create a new DNS configuration:
-
On the Sensor network configuration tab, create a new DNS configuration.
For example, name it ubisenseconfig.
-
Add up to four DNS IP addresses or DNS Suffixes or both, as required.
-
Review the details you have typed.
It is not possible to modify a DNS configuration after you save it. To modify an existing DNS configuration, delete it and then create a new configuration.
-
Save the DNS configuration.
- Assign the DNS configuration to the required devices. See Assigning Network Settings to Devices.
Each device will accept the DNS configuration only if it can validate the configuration by contacting a Location Platform server. If, after approximately ten minutes, it cannot validate the configuration, the device will revert back to the default network configuration. See Network Statuses.
Assigning Network Settings to Devices
All devices that currently do not have any custom network configuration are listed in the Default group. These devices use DHCP settings by default.
To assign custom network settings to a sensor or TDU:
- On the Sensor network configuration tab, select the required device.
-
The device can support a valid combination of settings, as listed in the following table.
IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway DNS Config Search Order - - - - 


- - - 

- - 


- 
- 

- 




- - 


- 





-
Save your settings.
The device is listed under the pending validation group until the static IP settings and/or DNS configuration are validated. If the settings are valid, the device is listed under the valid group.
If you left any fields blank, the device connects to the server as described in the following table.
| If you did not specify... | Behavior |
|---|---|
|
IP address and subnet mask |
The device connects to the Location Platform server by using DHCP. |
|
Default gateway |
|
|
DNS configuration |
|
|
Search order |
The device uses the default Ubisense search order. |
Network Statuses
After you have assigned network settings to a sensor or TDU, it appears under one of the network status groups that are listed in the following table.
| Network Status Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom (valid) | The device has successfully validated the network settings. |
| Custom (pending validation) | The network settings are awaiting validation from the device. |
| Custom (invalid) | The device could not validate the network settings. |
| Default | The device is using the default network configuration (DHCP). Custom network settings have not been specified. |
Deleting DNS Configurations and Search Orders
You can only delete DNS configurations and search orders that are currently not used by any device.
To delete an existing DNS configuration or search order:
-
Identify the devices that are currently using the specific DNS configuration or search order. Remove the DNS configuration or search order from the network settings of each device.
-
From the list of DNS Configurations, select the configuration that you want to delete, and then press the Delete key.
The DNS configuration is removed from the list.
Returning Sensors to their Default Network Settings
Sensors can become unusable if they were previously assigned a static IP address and then this configuration is no longer available to them. If this is the case, sensors with firmware version 1025 and above can be reset to use the default (DHCP) network settings. The reset button is on the rear of the sensor inside the enclosure and can be accessed via a hole in the rear casing by means of a paper-clip or other thin wire (see below).
To reset a sensor:
- Power-cycle the sensor and immediately press the reset button.
- Keep the reset button depressed for five seconds until the Sensor Status LED flashes red three times (taking a total time of about 15 seconds from power on).
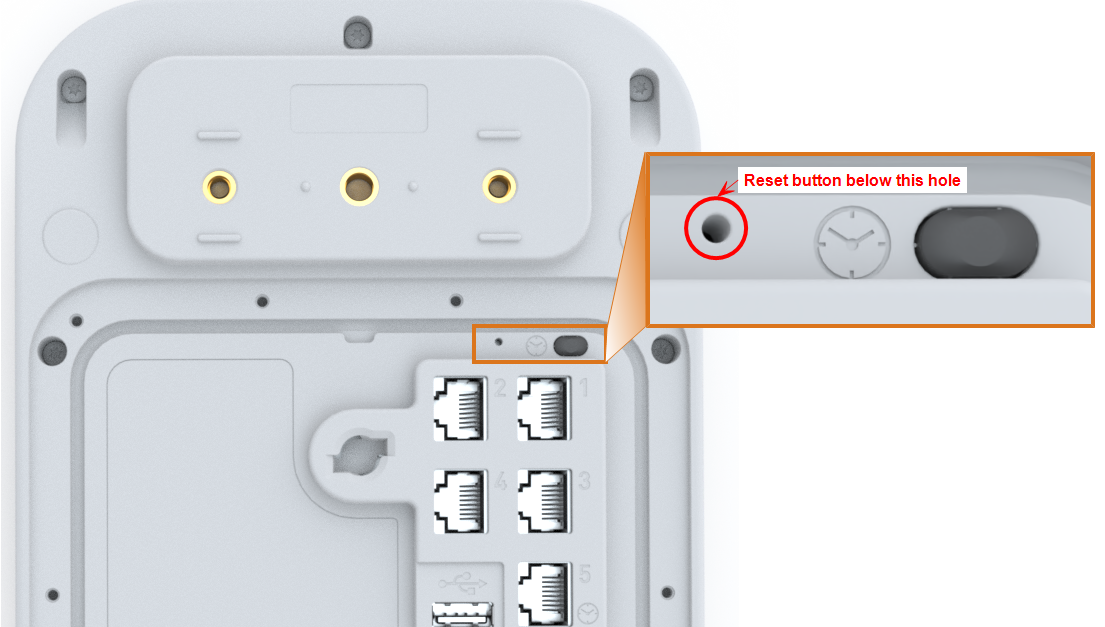
Rear View of a UWB Sensor with Access to the Reset Button Highlighted